On April 30, 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued a crucial Guidance Note on Operational Risk Management and Operational Resilience (RBI/2024-25/31 DOR.ORG.REC.21/14.10.001/2024-25). This guidance aims to significantly enhance the effectiveness of operational risk management of Regulated Entities (REs) and bolster their operational resilience amidst the complex, interconnected, and dynamic environment of the financial system.
Objectives of the Guidance
The primary objectives of the RBI’s guidance are two fold:
- Promoting Effective Operational Risk Management: Operational risk is inherent in all financial products, services, activities, processes, and systems. Effective management of these risks is essential for the overall stability and reliability of the financial system.
- Enhancing Operational Resilience: The guidance emphasizes the importance of REs being resilient to disruptions that can arise from various sources, including IT threats, geopolitical conflicts, business disruptions, frauds, technological failures, and natural disasters.
Operational Risk Management
Operational risk management is a critical component of an RE’s risk management framework. It reflects the effectiveness of the Board of Directors and Senior Management in overseeing the institution’s portfolio of products, services, activities, processes, and systems. Effective operational risk management involves:
- Identifying and Assessing Risks: Utilizing appropriate tools to identify and evaluate potential risks in a collaborative, co-ordinated manner.
- Monitoring Exposures: Keeping track of material operational exposures and any changes to them.
- Mitigating Risks: Implementing robust internal controls and risk management strategies to minimize operational disruptions and maintain the continuity of critical operations.
Operational Resilience
Operational resilience is the ability of an RE to continue delivering essential services in the face of disruptions. This requires a comprehensive risk assessment policy that includes:
- Man-Made Threats: Cyber-attacks, technological changes, and technology failures.
- Natural Causes: Climate change and pandemics.
- Other Disruptions: Internal/external frauds, business disruptions, and third-party dependencies.
The RBI guidance mandates that all REs must integrate these risks into their assessment frameworks and devise appropriate risk mitigation strategies to ensure operational resilience.
Three Lines of Defence
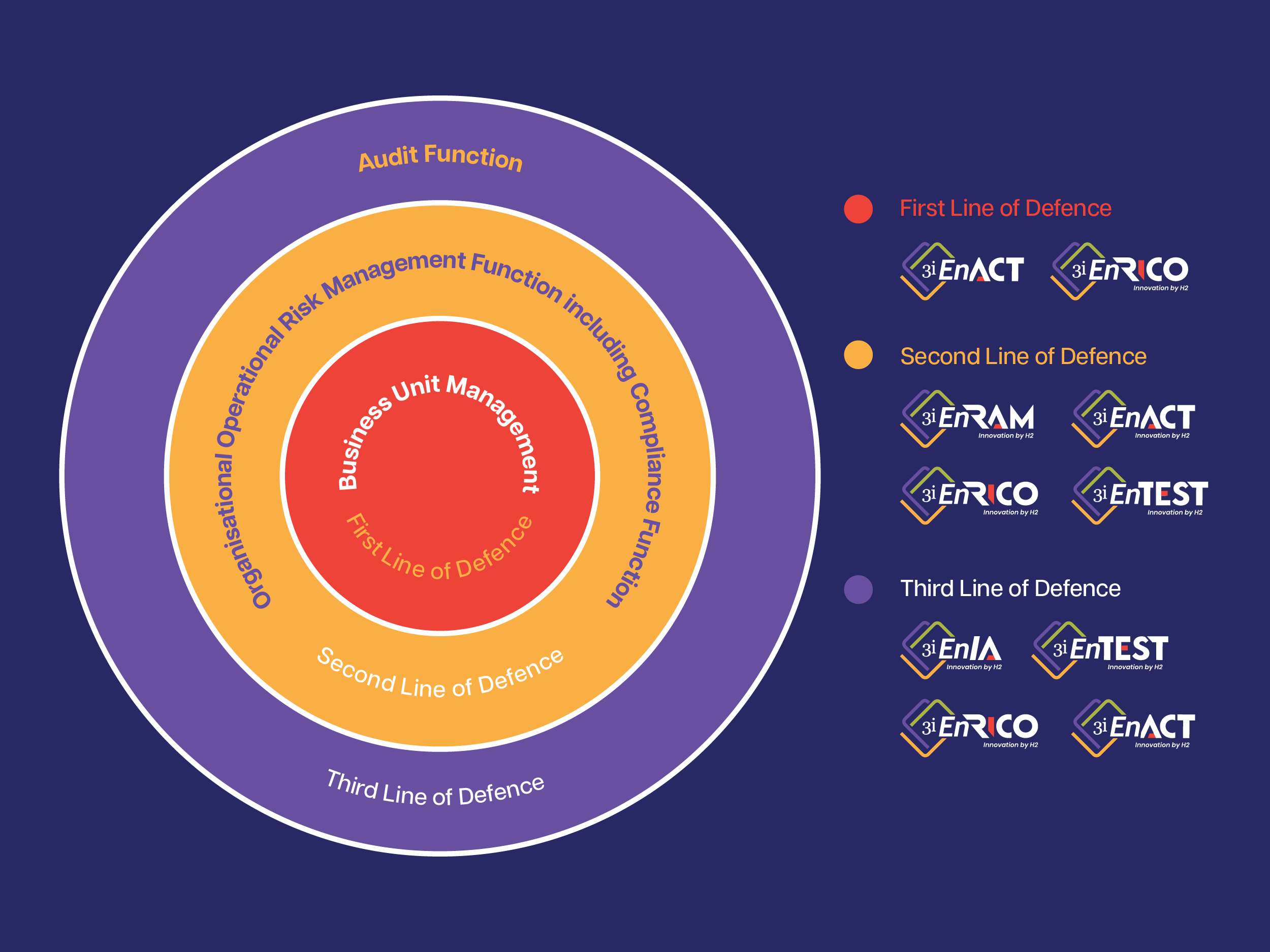
The RBI emphasizes a structured approach involving three lines of defence:
- First Line of Defence: Daily operations managed by all business units.
- Second Line of Defence: Risk and compliance functions within the organization.
- Third Line of Defence: The audit function ensuring thorough evaluation and accountability.
Pillars of Operational Risk and Resilience Management
The RBI identifies three pillars supporting a holistic approach to managing operational risk and resilience:
- Policy Compliance Assessment: Regular top-level reviews, verification of management controls, and resolution of non-compliance instances.
- Authorization and Accountability: Ensuring appropriate approvals and tracking deviations from policies and regulations.
- Feedback Loop: Continuously incorporating lessons learned during disruptions into the processes and executions.
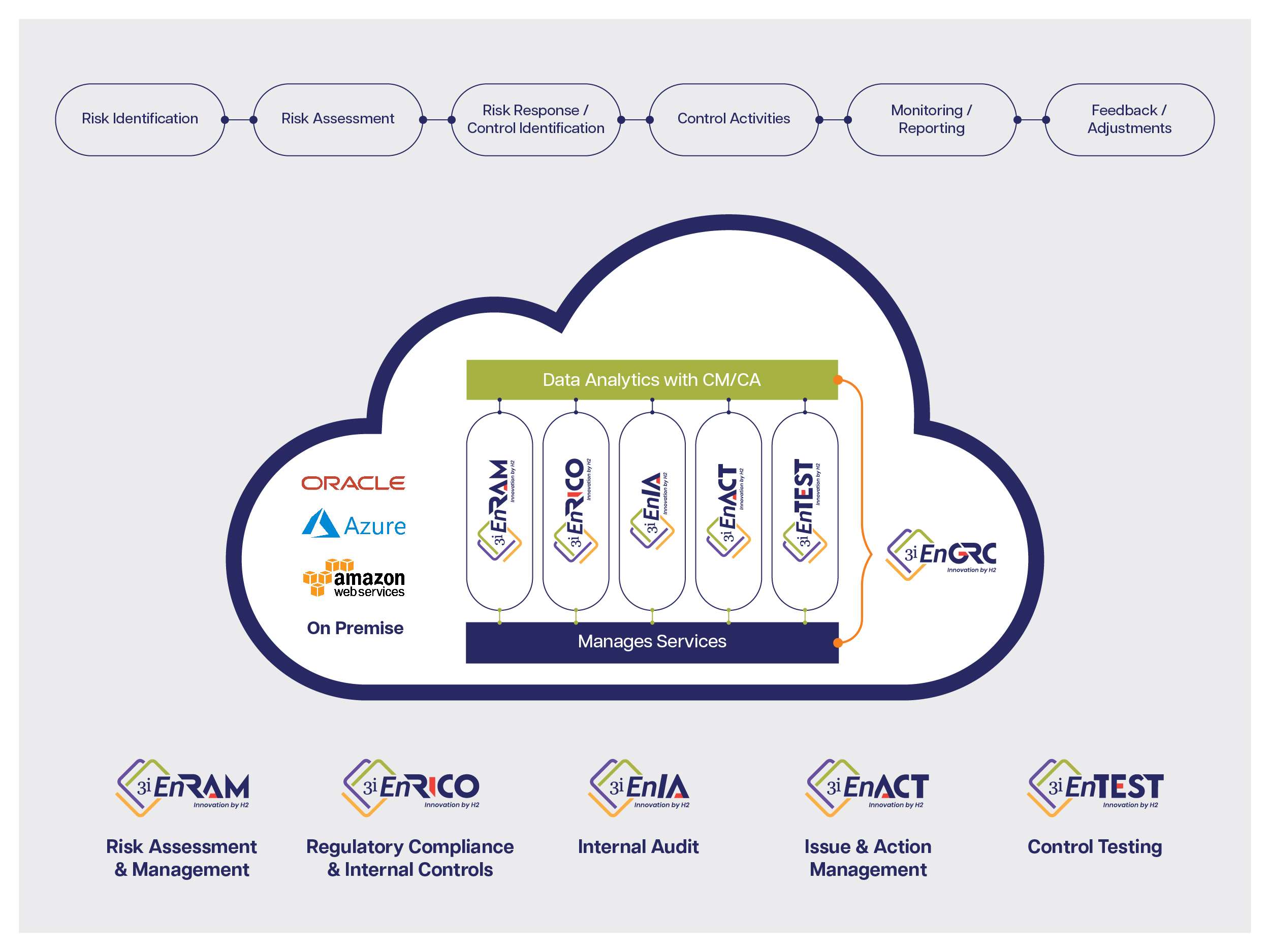
EnGRC’s Role in Achieving Compliance
EnGRC offers out-of-the-box functions to help REs adhere to the RBI guidance. Its modules leverage advanced technologies like blockchain, machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) to deliver robust risk management and operational resilience. Key features include:
- Automated Workflows/ Controls: Regular data checks without human intervention or automated workflows with reminders in cases where human intervention is necessary.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: High user adoption rates due to intuitive interface and design.
- Comprehensive Risk Management: Modules supporting the three lines of defence and enabling continuous mitigation and improvement cycles.
Steps for Robust Risk Management
- Identify Risks: Recognize financial, legal, operational, strategic, and reputational risks.
- Assess Risks: Use qualitative or quantitative methods tailored to organizational needs.
- Develop a Risk Management Plan: Define risk response strategies, allocate resources, and establish communication and monitoring mechanisms.
- Implement the Plan: Ensure all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities, and regularly review and update the plan.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously assess the plan’s effectiveness, identify new risks, and adjust as necessary.
Conclusion
Robust risk management and operational resilience are critical for the long-term success of REs. By adhering to the RBI’s guidance and leveraging solutions like EnGRC, organizations can effectively manage potential risks, enhance their reputation, and maintain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. For more information on how EnGRC can support your risk management needs, visit EnGRC – Enterprise Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) Solution.